What Is a Recession | Recession Definition and What a Recession Means in the Economy

Economic ups and downs are normal parts of financial cycles, yet few terms create more concern than recession. Many beginners ask the same questions. What is a recession? What is a recession in the economy? What is the official recession definition? Understanding these concepts helps individuals make smarter financial choices and prepare for economic uncertainty. This guide explains everything in a simple, practical, and beginner-friendly way.
Recession Definition
A recession is a significant decline in economic activity that lasts for several months or longer. As explained by Investopedia, recessions affect spending, business profits, employment, and financial market confidence. A recession forms when multiple sectors weaken at the same time, creating a broad slowdown across the economy.
Key Characteristics of a Recession
➔ Slower economic growth
➔ Higher unemployment
➔ Decline in consumer spending
➔ Weaker business performance
➔ Lower industrial production
➔ Widespread financial uncertainty
These indicators together signal a meaningful decline in economic activity.

What Is a Recession in the Economy
When people ask what is a recession in the economy, they refer to a period where households, businesses, and markets all experience reduced activity. Recessions influence daily life, corporate decision-making, and government policies.
How a Recession Impacts the Economy
➔ People spend less because they feel uncertain about the future.
➔ Businesses earn less and cut costs.
➔ Companies reduce hiring or lay off workers.
➔ Investments slow down across industries.
➔ Government tax revenues decline.
As noted by Forbes, recessions affect almost every part of the economy, often requiring careful planning and strategic financial behavior. During such uncertain periods, many investors choose to practice risk-free first using a demo account before committing real capital.
What Causes a Recession
Recessions rarely have a single cause. Instead, they develop when multiple weaknesses overlap.
Common Causes
➔ High inflation reduces purchasing power.
➔ Rising interest rates make borrowing more expensive.
➔ Financial crises disrupt banks or markets.
➔ Global events such as wars or pandemics reduce activity.
➔ Asset bubbles burst after periods of overvaluation.
➔ Falling confidence leads consumers and businesses to spend less.
According to The Balance, recessions are natural parts of long-term economic cycles.
How Economists Confirm a Recession
Economists look at several indicators to confirm a recession. It is never based on one number alone.
Indicators Used
Gross Domestic Product – Measures total economic output.
Employment levels – Reflect labor market strength.
Consumer spending – Shows household confidence and demand.
Industrial production – Signals manufacturing activity.
Retail sales – Tracks real-world buying behavior.
Business investment – Reveals corporate growth expectations.
When several of these indicators weaken at the same time, the economy may be entering a recession.
Types of Recessions
Recessions can follow different patterns depending on their underlying cause.
➔ Demand-Driven Recession – When consumers suddenly reduce spending.
➔ Supply Shock Recession – When production is disrupted by supply shortages.
➔ Balance Sheet Recession – When excessive debt forces spending cuts.
➔ Structural Recession – Caused by long-term economic changes.
Each type influences industries differently and requires unique policy responses.
Early Warning Signs of a Recession
Recessions often show early signals before fully unfolding.
Warning Indicators
➔ Rising unemployment
➔ Slower retail spending
➔ Declining manufacturing output
➔ Weak housing activity
➔ Falling consumer confidence
➔ Tighter bank lending
Monitoring these trends helps individuals and businesses prepare earlier.
How Recessions Affect Individuals
Recessions influence daily life in ways that directly impact financial stability and personal decisions.
Effects on Individuals
➔ Increased job insecurity
➔ Reduced income
➔ Greater pressure on household budgets
➔ Lower investment returns
➔ Slower wage growth
➔ More cautious spending habits
This is why many traders choose to gain experience in volatile conditions through simulation before deciding to open a real trading account.
How Recessions Affect Businesses
Businesses must adapt quickly to survive periods of declining demand.
Business Impacts
➔ Lower sales
➔ Reduced profits
➔ Hiring freezes
➔ Cancelled expansion plans
➔ Stricter cost controls
➔ Higher operational risk
Companies with strong cash flow and flexibility tend to navigate recessions more effectively.
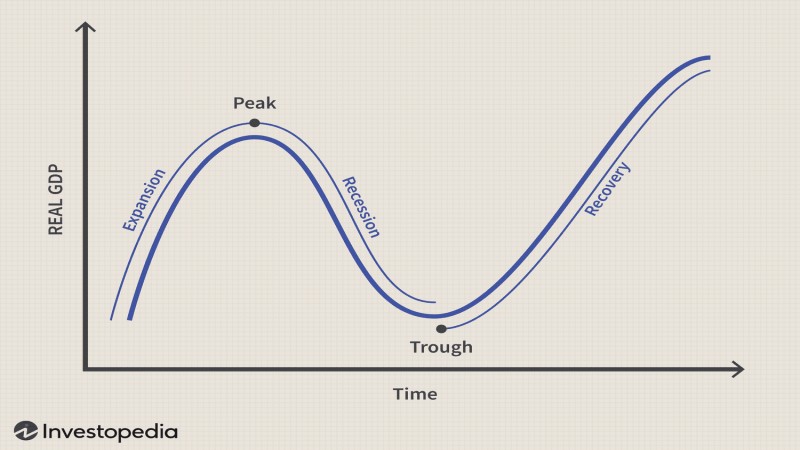
Recession and Financial Markets
Markets often react strongly to recession fears. Investor sentiment turns cautious, causing capital to shift across asset classes.
Market Reactions
➔ Increased stock market volatility
➔ Higher demand for safe-haven assets such as gold and bonds
➔ Slower overall market growth
➔ Reduced appetite for high-risk assets
Professional trading platforms such as Ultima Markets offer tools that help investors respond more strategically to shifting market conditions during economic downturns.
Strategies to Prepare for a Recession
Preparation reduces financial risk and strengthens long-term stability.
Smart Financial Strategies
➔ Build an emergency fund
➔ Reduce high-interest debt
➔ Diversify investments
➔ Prioritize essential expenses
➔ Strengthen job skills
Being prepared allows individuals to face economic uncertainty with greater confidence.
Does Every Recession Lead to a Crisis
Not all recessions turn into severe economic crises. Some are short and mild, while others are deep and prolonged.
Factors That Determine Severity
➔ The root cause of the recession
➔ Government stimulus measures
➔ Central bank monetary policy
➔ Economic diversity
➔ Business balance sheet strength
Understanding these elements helps investors interpret economic developments more clearly.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Understanding what is a recession and knowing the official recession definition helps individuals navigate uncertainty with greater clarity. Learning what is a recession in the economy strengthens financial literacy and supports better long-term decision-making.

Key Takeaways
➔ A recession is a broad decline in economic activity.
➔ It impacts employment, spending, investments, and markets.
➔ Recessions arise from inflation, financial instability, and global events.
➔ Early warning signs allow better preparation.
➔ Financial readiness reduces household and business risk.
➔ Platforms like Ultima Markets support investors through economic cycles.
“The best time to prepare is before the storm arrives.”
Recessions are challenging, but understanding how they work empowers individuals to stay financially resilient.






